🌍 What Makes Bitcoin Different from Traditional Money?
Imagine a world where sending money is as easy as sending an email. This is the reality with Bitcoin, a type of digital currency that operates without the need for a central authority, like a bank or government. Unlike traditional money, which is printed and controlled by governments, Bitcoin is created and managed through a process called mining, a complex operation where computers solve difficult puzzles to secure transactions. What’s remarkable about Bitcoin is its limited supply; there will only ever be 21 million Bitcoins, making it immune to inflation, unlike regular currencies that can be printed endlessly. This digital currency allows for direct transactions between two parties, thanks to a technology called blockchain, which records all transactions in a public ledger, ensuring security and transparency. Here’s a simple comparison to summarize the differences:
| Feature | Bitcoin | Traditional Money |
|---|---|---|
| Authority | Decentralized (No central control) | Centralized (Governments, Banks) |
| Creation | Mining (Fixed Supply) | Printing (Unlimited Supply) |
| Transaction Method | Direct (Peer-to-Peer) | Intermediary (Through Banks) |
| Inflation | Resistant | Subject to inflation |
This ingenuity makes Bitcoin a groundbreaking digital asset that challenges the very fabric of how traditional money is used and perceived in our global economy.
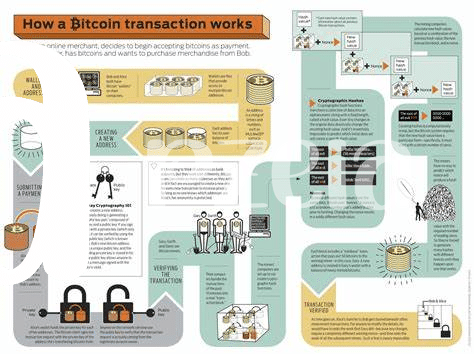
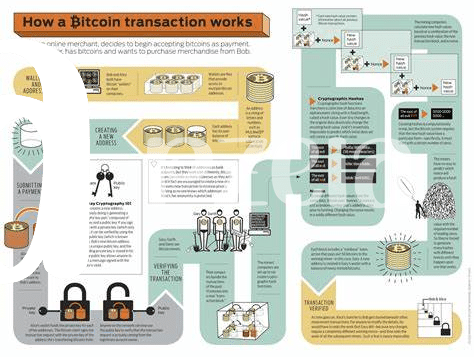
🛠️ How Bitcoin Transactions Work: a Simple Breakdown
Imagine sending money to a friend, but instead of using a bank, you’re using your phone, and the transaction is secure, with no middlemen. That’s a bit like how Bitcoin transactions work. Each transaction is a digital packet of information, including the amount of Bitcoin you’re sending, the recipient’s address, and your digital signature, which proves the transaction is legitimate. This bundle of information then gets sent out to a vast network of computers, known as the blockchain.
On the blockchain, this information is verified and added to a public ledger, an open book for all to see, ensuring transparency and security. If you’re curious about how this transparency plays into the bigger picture of Bitcoin’s benefits, especially in charitable activities, check out this deep dive into public ledgers. The process might sound complex, but it’s this innovative approach that removes the need for traditional financial institutions, allowing for faster, cheaper, and more democratic transactions.
💸 Understanding Bitcoin Fees: the Basics

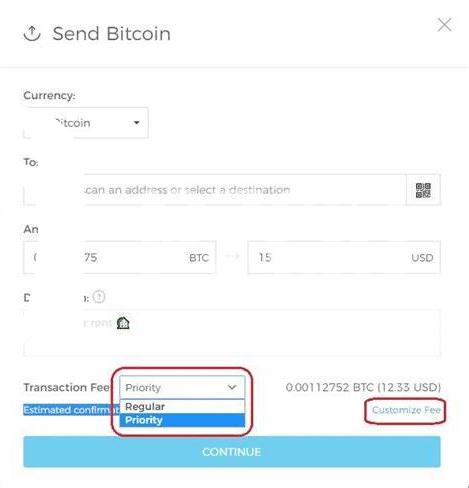
When you send someone Bitcoin, it’s not like handing over cash directly from your pocket to theirs. There’s a bit more going on behind the scenes. You’re actually asking a network of computers around the world to update the record of who owns the Bitcoin. These computers, which work hard to keep everything running smoothly, don’t do this for free. They require a fee for their services. This fee is what we call a Bitcoin transaction fee. It’s a bit like a tip for the network’s miners who validate and secure your transaction on the blockchain, Bitcoin’s digital ledger.
The amount of this fee isn’t fixed; it changes depending on a few things. 🤔 First up, it’s about how busy the network is. Think of it as a highway; the more cars (or transactions) there are, the slower everything goes unless you pay a bit more to get into the fast lane. Another factor is how much data your transaction takes up. A bigger transaction can be like a larger vehicle taking up more space on the road, potentially costing more to move. These fees ensure your transaction is processed by the network in a timely manner, keeping the digital highway of Bitcoin smooth and efficient. 🚗💨
📈 Factors Influencing Your Bitcoin Transaction Costs
When you send or receive bitcoin, you might notice that the cost can vary quite a bit. So, what’s behind these changes in price? Picture this: Bitcoin is like a digital highway. During rush hour, when loads of people are sending bitcoin, traffic clogs up, making everything slower and more expensive. This is because miners – the folks working behind the scenes to confirm transactions and keep the bitcoin network running smoothly – pick the transactions with higher fees first. It’s a bit like tipping for faster service. The size of your transaction plays a role too. Bigger transactions take up more space on the blockchain, the technology underpinning bitcoin, meaning they can cost more to process. Another factor is how jam-packed the bitcoin network is. If it’s a busy day, fees can skyrocket. But on quieter days, moving your bitcoin can be cheaper. Interestingly, the technology and rules of bitcoin can change, affecting how we think about fees in the future. For a closer look at how bitcoin’s design influences things like transaction costs, dive into the role of public ledgers in bitcoin’s transparency versus ethereum. Finally, savvy strategies, like timing your transaction when the network is less busy or adjusting the fee you’re willing to pay, can help keep costs down. So, keeping an eye on these factors can be handy for anyone looking to move bitcoin without spending too much in fees.
🚀 Tips to Minimize Fees and Save Money
When looking to keep more coins in your virtual wallet, understanding how to manage transaction fees can make all the difference. One key strategy is selecting the right timing. Just like traffic on the road, the Bitcoin network can get busy, and these peak times drive up fees. By choosing off-peak times for your transactions, you might just find yourself paying less. Another savvy move is to adjust your fee settings. Many wallets allow you to choose the speed of your transaction; opting for a slower transaction time can lead to lower fees. Also, keeping an eye out for SegWit (Segregated Witness) transactions—these are a type of transaction that can reduce your fees. Lastly, consolidating your transactions can be a game-changer. By sending multiple payments at once, you decrease the total cost. Here’s a quick guide to help you remember:
| Tip | How It Helps |
|---|---|
| Choose off-peak times | Lower fees by avoiding busy times on the network |
| Adjust fee settings | Opt for slower transactions to save money |
| Use SegWit transactions | Benefit from a more efficient transaction format |
| Consolidate transactions | Send multiple payments at once to reduce costs |
These straightforward steps can significantly influence how much you spend on transaction fees, leaving you with more Bitcoin to enjoy or invest.
🔍 Future of Bitcoin Fees: What to Expect
Looking ahead, the landscape of Bitcoin fees might seem a bit foggy, but there’s plenty to be optimistic about. With advancements in technology and a growing acceptance of cryptocurrencies, we’re likely to see changes that could make Bitcoin transactions quicker and cheaper. Innovations like the Lightning Network are already working to speed things up by allowing transactions to occur off the main blockchain, thus reducing congestion and, by extension, fees. Plus, as more people use Bitcoin, understanding how to navigate the fee market becomes a handy skill, helping users to optimize their transaction costs even further.
At the same time, the role of Bitcoin in global philanthropy is evolving, showing us the growing impact of cryptocurrencies beyond just investment or payment methods. For those interested in delving deeper into how Bitcoin supports philanthropic initiatives globally versus Ethereum, mastering bitcoin technical analysis for profitable trading versus Ethereum becomes crucial. This comparative analysis not only highlights the unique advantages each platform offers to charitable causes but also equips donors and activists with the knowledge to make informed decisions about their contributions, solidifying the role of digital currencies in creating positive change worldwide.
