🌏 Introduction to Bitcoin and Cryptocurrency Basics
Imagine a world where digital money exists, much like the coins and banknotes in your wallet, but it’s stored on computers all around the globe. This is the essence of cryptocurrency, with Bitcoin leading the march. It’s a form of money that’s entirely online, allowing people to send and receive funds directly to each other, without needing a middleman like a bank. The beauty of it is not just its digital nature but also how it ensures that all transactions are secure and recorded on a public ledger known as the blockchain.
Turning our focus specifically to Bitcoin, we find it’s not just another digital currency; it’s the pioneer that introduced many to the world of cryptocurrencies. Here’s a simple breakdown:
| **Term** | **Description** |
|——————-|———————————————————————————————————|
| Cryptocurrency | Digital or virtual money, uses cryptography for security. |
| Bitcoin | The first and most well-known cryptocurrency, introduced in 2009. |
| Blockchain | A digital ledger where transactions made in Bitcoin or another cryptocurrency are recorded chronologically and publicly. |
Through its innovative use of blockchain technology, Bitcoin enables a secure, transparent, and decentralized way of managing digital transactions, without the oversight of central authorities. This has opened up a new frontier in the way we think about money and financial transactions in the digital age.
💪 Understanding Proof of Work and Its Role
Imagine a big digital ledger where every transaction needs a unique key to be confirmed. This is what Proof of Work (PoW) helps with in Bitcoin. It’s like a big puzzle-solving contest. Computers from all over the world compete to solve a complex math problem first. The winner gets to add a new block of transactions to the blockchain, the ledger, and as a reward, they receive some Bitcoin. This process makes sure that all transactions are secure and no one tries to spend their Bitcoins twice. However, it requires a lot of energy because all those computers are working hard to solve the puzzles. While this might sound complicated, it’s an essential part of how Bitcoin keeps its network safe and transparent. If you’re curious about how Bitcoin aims to make its operations safer and more accessible for people without bank accounts, check out https://wikicrypto.news/unbanked-and-thriving-exploring-bitcoin-as-a-solution.
⚖️ Exploring Proof of Stake and How It Differs

Imagine a world where instead of spending tons of energy to prove you’ve done some hard work, you could simply show you have a stake in the game, a bit like holding a golden ticket that says, “Trust me, I’ve got a part in this.” That’s the essence of Proof of Stake (PoS). Unlike its energy-hungry cousin, Proof of Work (PoW), which powers Bitcoin, PoS operates on a principle somewhat akin to a raffle draw. Here, the more tickets (or stake) you hold, the higher your chances of being chosen to validate transactions and create new blocks. It’s a system that asks for your investment in the network as a form of trust, rather than making you solve complex puzzles. This approach not only reduces the colossal amount of energy required but also opens the door for more people to participate without needing supercomputers. It’s akin to being part of an exclusive club where your membership level affects your chances of getting to make important decisions. This variation brings a different flavor to the crypto world, suggesting a future where the digital currency landscape could be more environmentally friendly and inclusively governed.
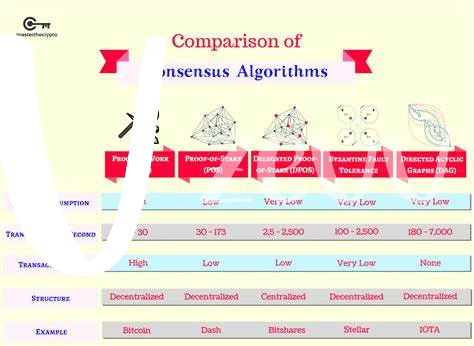
🔋 Energy Consumption: Comparing the Two Models

When we talk about how much energy these systems use, it’s a bit like comparing a truck to a bicycle. Proof of Work (PoW), the method Bitcoin uses, is the truck. It requires a lot of computational power to solve complex puzzles, which in turn means a lot of electricity. Imagine a room full of supercomputers all trying to solve a very difficult puzzle first. This energy use has raised concerns about the environmental impact. On the other hand, Proof of Stake (PoS) is more like the bicycle. It chooses validators to confirm transactions based on the number of coins they hold and are willing to “stake” as collateral. It’s a process that requires significantly less energy, making it a greener alternative.
Both methods aim to keep the network secure and decentralized, but they approach the energy question very differently. With increasing awareness about climate change and sustainability, the conversation around these methods’ energy consumption has become increasingly important. For those just getting started and looking to understand how Bitcoin fits into the digital world, including its energy consumption nuances, checking out resources like bitcoin paper wallets for beginners can offer valuable insights. The journey towards a more sustainable digital finance world is ongoing, and the paths of PoW and PoS represent different forks in this road.
🤝 Security and Decentralization in Pow Vs. Pos
In the digital world of cryptocurrencies, how they keep their networks safe and run fairly is a big deal. Imagine two neighborhoods, each with its own way of keeping peace and fairness. One relies on a group of dedicated guards (Proof of Work, or PoW) who work day and night, solving complex puzzles to validate transactions and in return, they receive rewards. This method is like a marathon where the fastest and strongest win, but it needs a lot of energy. On the other hand, Proof of Stake (PoS) is like a council of citizens, chosen based on how much currency they hold and are willing to “stake” as a form of security deposit. These chosen ones get to validate transactions and earn rewards, but without the need for extensive energy use.
| Feature | PoW | PoS |
|---|---|---|
| Security | High from energy-intensive computations | High from staked investments as security |
| Decentralization | Can be centralizing due to mining pools | More evenly distributed, depending on the algorithm |
| Energy Consumption | Very High | Low |
Choosing between PoW and PoS affects not only the security and fairness of a cryptocurrency but also its impact on our planet. As we look into their future, it’s like deciding between two paths in a forest, both leading to unknown destinations, each with its own set of challenges and promises.
🚀 Future Outlook: Which Path Will Bitcoin Take?
As we peer into the crystal ball of Bitcoin’s journey, the choice between Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS) seems to be more than just a technical crossroad; it’s a reflection of what we envision for the future of currency. On one hand, PoW, the method currently powering Bitcoin, has proven its strength and resilience over the years, safeguarding the network against attacks and ensuring every transaction is verified with the computational work of miners. On the other hand, PoS presents itself as a newer, shinier path with the promise of lower energy consumption and faster, cheaper transactions. The debate is not just about efficiency or security, but about which path aligns with the ethos of decentralization and empowerment, especially for the unbanked, for whom Bitcoin holds the promise of financial inclusion.
The direction Bitcoin will take could reshape the landscape of digital currency, influencing not only those who mine or invest but also those who look to Bitcoin for a beacon of financial autonomy. As we navigate this journey, learning the ropes of how Bitcoin operates becomes crucial. For beginners eager to dip their toes into the world of cryptocurrency, understanding the underlying mechanisms can be simplified by exploring bitcoin technical analysis for beginners. The choice between PoW and PoS is more than a technical decision; it’s a chapter yet to be written in the annals of digital currency, holding the potential to redefine the balance between security, efficiency, and inclusivity.
